Unveiling the Reality of 30 Day Liquid Diet Weight Loss Results
Embarking on a weight loss journey can be both exciting and overwhelming, especially with countless diet plans promising rapid results. Among these, the 30-day liquid diet has surged in popularity for its promise of swift weight loss. But what does science say about its effectiveness and safety? In this comprehensive guide, we explore the 30-day liquid diet weight loss results, delving into the types of liquid diets, expected outcomes, potential benefits, and associated risks. Whether you’re considering this approach or simply curious, this article offers valuable insights backed by scientific research to help you make an informed decision.

Understanding Liquid Diets
Types of Liquid Diets
Liquid diets replace solid foods with liquids to achieve various health and weight loss goals. They generally fall into three categories:
- Full Liquid Diets
Include all liquids and foods that turn to liquid at room temperature, such as milk, fruit juices, creamy soups, and ice cream. These diets are often used post-surgery or during illness when solid food intake is challenging. - Clear Liquid Diets
Consist of transparent liquids like broth, gelatin, and clear juices, often used for short-term purposes or medical reasons, such as before certain medical procedures. These diets provide minimal calories and nutrients. - Meal Replacement Liquid Diets
Utilize specialized shakes and supplements to replace one or more meals daily, aiming for balanced nutrition. These diets are designed for weight loss and often include added vitamins and minerals to ensure nutritional adequacy.
Calorie Content in Typical Liquid Diets
Calorie intake varies significantly across different liquid diets. A typical 30-day liquid diet might range from 800 to 1,200 calories per day, significantly lower than the average daily requirement of 2,000 calories for women and 2,500 for men. This substantial calorie reduction is a primary driver of weight loss but must be carefully managed to avoid nutritional deficiencies. For example, a study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that participants on a 1,000-calorie liquid diet lost an average of 10 pounds in one month, highlighting the effectiveness of calorie restriction.
Nutritional Considerations
While liquid diets can be effective for weight loss, they may lack essential nutrients such as fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It’s crucial to ensure that the diet is balanced and, if necessary, supplemented with vitamins or minerals to meet daily nutritional needs. According to the American Dietetic Association, inadequate nutrient intake can lead to health issues like weakened immunity, bone loss, and decreased muscle mass. Therefore, incorporating multivitamins or specific supplements is often recommended to maintain overall health during the diet period.
The 30 Day Liquid Diet Plan
A successful 30-day liquid diet plan requires careful planning to ensure nutritional balance, maintain energy levels, and support overall health. Below is a detailed breakdown of how to structure your 30-day liquid diet, including a week-by-week guide, sample menus, recipes, and practical tips to enhance adherence and effectiveness.
Structure of a Typical 30-Day Plan
A 30-day liquid diet plan usually involves replacing two meals per day with liquid alternatives while maintaining one solid meal. This structure helps reduce overall calorie intake while still providing some solid food to maintain digestive health. Here’s a general framework:
- Breakfast: Liquid meal (e.g., smoothie or protein shake)
- Lunch: Liquid meal (e.g., soup or meal replacement shake)
- Dinner: Solid meal (e.g., lean protein with vegetables)
- Snacks: Optional liquid snacks (e.g., smoothies or yogurt drinks)
Week-by-Week Breakdown
Week 1: Transition Phase
Goal: Ease into the liquid diet, allowing your body to adjust to the reduced calorie intake and increased liquid consumption.
- Breakfast: Smoothie with almond milk, banana, spinach, and protein powder.
- Lunch: Blended vegetable soup with added protein powder.
- Dinner: Grilled chicken breast with steamed broccoli and carrots.
- Snacks: Greek yogurt smoothie with berries.
Tips:
- Start by gradually reducing solid food portions.
- Increase water intake to stay hydrated.
- Incorporate light exercise, such as walking or yoga.
Week 2: Stabilization Phase
Goal: Establish a routine and ensure you’re meeting nutritional needs through liquid meals.
- Breakfast: Protein shake with oat milk, mixed berries, and chia seeds.
- Lunch: Pureed lentil soup with added vegetables and a scoop of protein powder.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with quinoa and steamed asparagus.
- Snacks: Green smoothie with kale, apple, and cucumber.
Tips:
- Monitor your energy levels and adjust calorie intake if necessary.
- Introduce a variety of liquids to prevent monotony.
- Continue regular physical activity to support weight loss.
Week 3: Optimization Phase
Goal: Enhance the diet with nutrient-dense liquids and ensure muscle preservation.
- Breakfast: High-protein smoothie with Greek yogurt, banana, spinach, and whey protein.
- Lunch: Creamy tomato soup with added vegetables and protein powder.
- Dinner: Turkey meatballs with mashed sweet potatoes and green beans.
- Snacks: Avocado smoothie with almond milk and a touch of honey.
Tips:
- Incorporate resistance training exercises to preserve muscle mass.
- Ensure each liquid meal contains a balance of proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
- Listen to your body and address any signs of fatigue or nutrient deficiencies.
Week 4: Maintenance and Preparation for Transition
Goal: Prepare to transition back to solid foods while maintaining weight loss and nutritional balance.
- Breakfast: Protein-packed smoothie with berries, spinach, flax seeds, and protein powder.
- Lunch: Pureed vegetable and chickpea soup with added herbs.
- Dinner: Grilled tofu with quinoa and mixed vegetables.
- Snacks: Herbal tea with a protein-rich yogurt drink.
Tips:
- Start planning how to reintroduce solid foods gradually.
- Maintain balanced macronutrient intake to support metabolic health.
- Reflect on your progress and set long-term weight maintenance goals.
RELATED: 13 Salt Water Trick for Weight Loss
Detailed Sample Menu and Recipes
Day 1 Sample Menu
Breakfast:
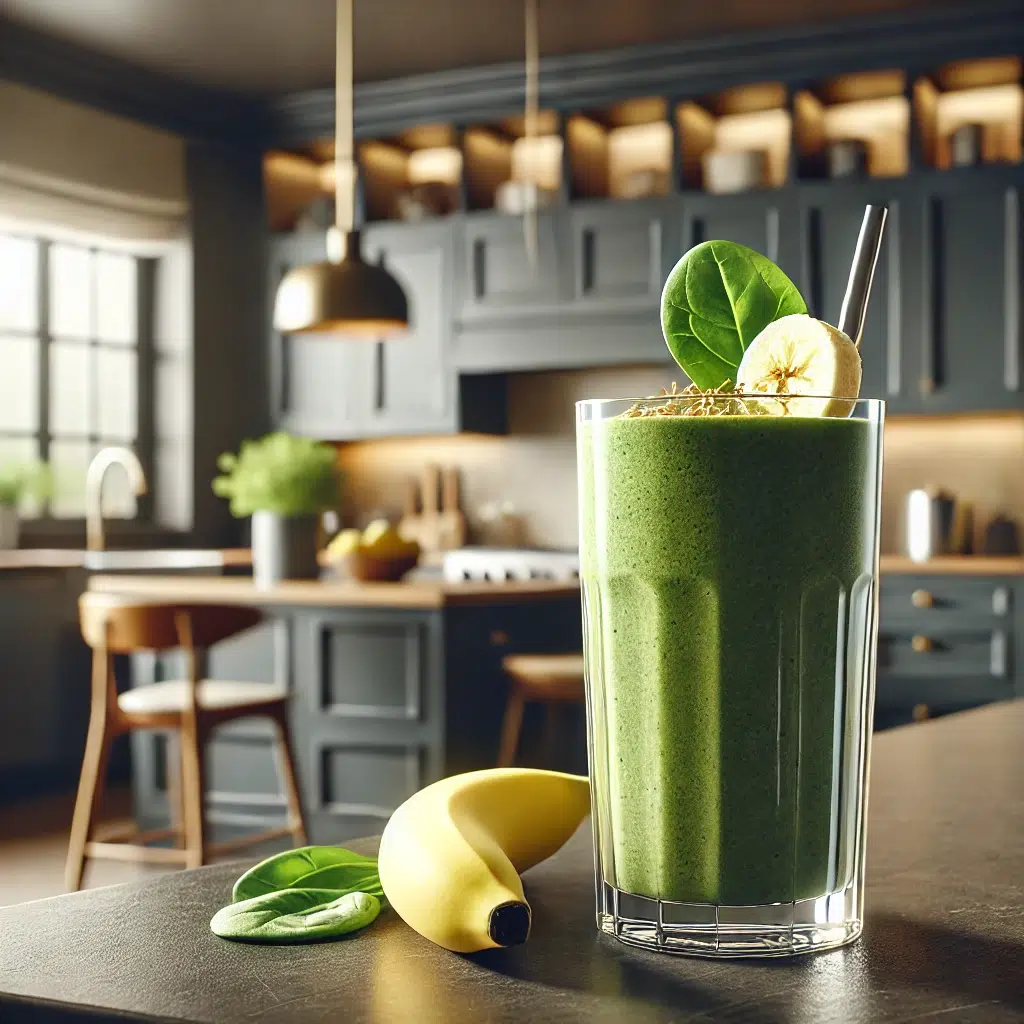

- Banana Spinach Protein Smoothie
Ingredients:- 1 banana
- 1 cup spinach
- 1 scoop whey protein
- 1 cup almond milk
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
Instructions: Blend all ingredients until smooth.
Nutritional Info: Approximately 350 calories, 25g protein, 45g carbohydrates, 10g fat.
Lunch:
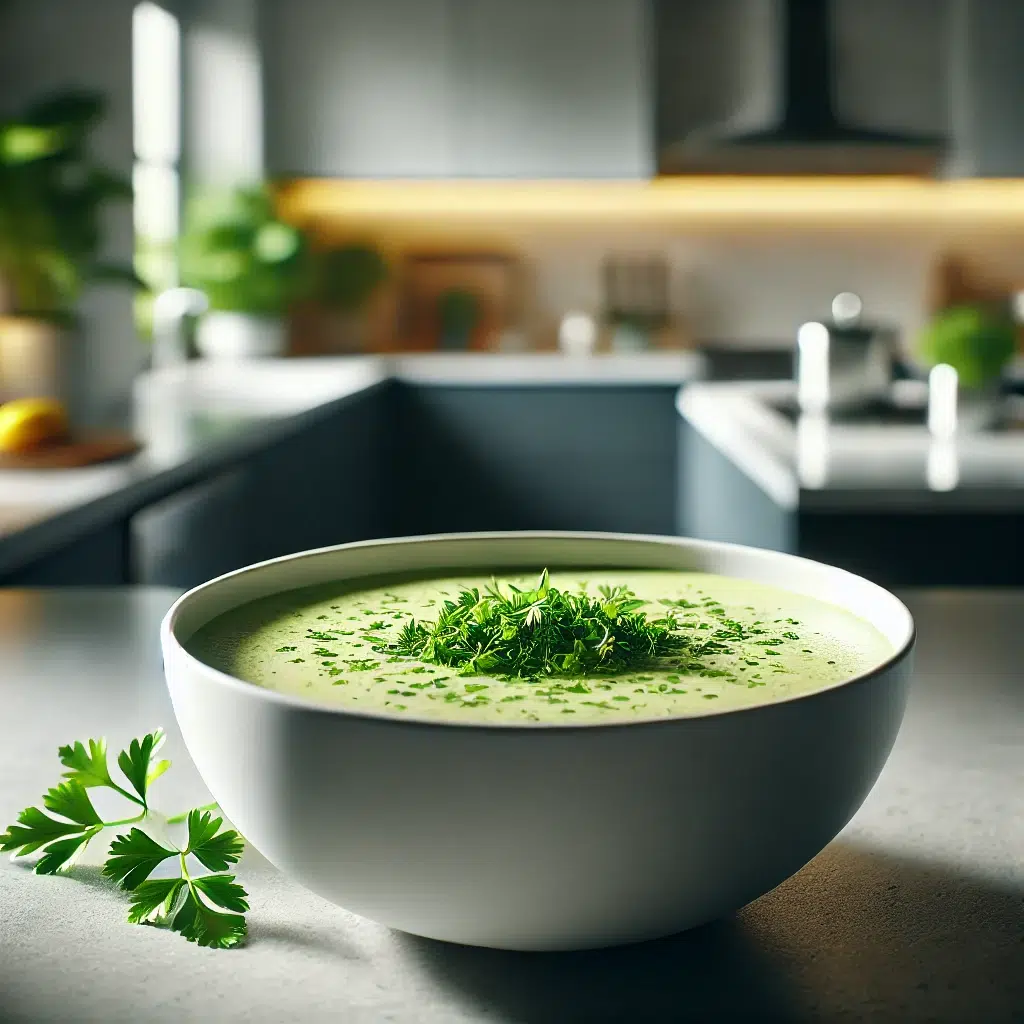

- Creamy Vegetable Soup
Ingredients:- 2 cups mixed vegetables (carrots, celery, tomatoes)
- 1 scoop unflavored protein powder
- 4 cups vegetable broth
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions: Cook vegetables in broth until tender. Blend until smooth and stir in protein powder. Season as desired.
Nutritional Info: Approximately 300 calories, 20g protein, 40g carbohydrates, 5g fat.
Dinner:
- Grilled Chicken with Steamed Vegetables
Ingredients:- 6 oz grilled chicken breast
- 1 cup steamed broccoli
- 1 cup steamed carrots
Instructions: Grill chicken until fully cooked. Steam vegetables and serve alongside.
Nutritional Info: Approximately 450 calories, 40g protein, 20g carbohydrates, 15g fat.
Snacks:
- Berry Greek Yogurt Smoothie
Ingredients:- 1/2 cup Greek yogurt
- 1/2 cup mixed berries
- 1 teaspoon honey
Instructions: Blend all ingredients until smooth.
Nutritional Info: Approximately 150 calories, 10g protein, 25g carbohydrates, 2g fat.
Week 2 Recipe: Protein-Packed Green Smoothie
Ingredients:
- 1 cup kale
- 1 green apple, cored
- 1 cucumber
- 1/2 avocado
- 1 scoop plant-based protein powder
- 1 cup coconut water
Instructions:
- Add all ingredients to a blender.
- Blend until smooth.
- Serve immediately.
Nutritional Info: Approximately 400 calories, 25g protein, 50g carbohydrates, 15g fat.
Recommended Supplements and Additives
To ensure nutritional adequacy during the 30-day liquid diet, consider incorporating the following supplements:
- Multivitamins: To cover any potential gaps in vitamins and minerals.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Supports heart health and reduces inflammation.
- Fiber Supplements: Aids digestion and prevents constipation.
- Electrolytes: Maintains electrolyte balance, especially if engaging in regular exercise.
- Protein Powder: Ensures adequate protein intake to preserve muscle mass.
Example Supplement Schedule:
- Morning: Multivitamin with breakfast smoothie.
- Afternoon: Omega-3 supplement with lunch soup.
- Evening: Fiber supplement with dinner.
- Pre-Bed: Protein shake if additional protein is needed.
Practical Tips for Success
- Meal Prep: Plan and prepare your liquid meals in advance to ensure consistency and reduce the temptation to deviate from the plan.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and support metabolic processes.
- Variety: Incorporate a wide range of liquid foods to prevent boredom and ensure a broad spectrum of nutrients.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to hunger cues and energy levels. Adjust portion sizes or supplement as needed.
- Support System: Engage with a support group or a nutritionist to stay motivated and receive professional guidance.
- Monitor Progress: Keep a journal of your meals, weight loss progress, and how you feel to track effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
RELATED: Unlock 7 Effective Coffee Hacks for Weight Loss Success
Expected Weight Loss Results
Average Weight Loss in 30 Days
On average, individuals following a 30-day liquid diet can expect to lose between 8 to 12 pounds. However, results can vary based on factors like starting weight, adherence to the diet, and individual metabolism. A clinical trial published in Obesity Research reported that participants on a liquid diet lost an average of 10 pounds in the first month, with some losing up to 15 pounds. It’s important to note that initial weight loss is often a combination of fat, muscle, and water weight.
Factors Affecting Weight Loss Outcomes
Several factors influence weight loss outcomes, including:
- Age: Younger individuals tend to have higher metabolic rates, leading to faster weight loss.
- Gender: Men generally lose weight faster than women due to higher muscle mass.
- Physical Activity Level: Incorporating exercise can enhance weight loss and preserve muscle mass.
- Metabolic Rate: Individuals with higher metabolism may lose weight more quickly.
- Diet Composition: The balance of macronutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) affects satiety and energy levels.
- Adherence: Consistently following the meal plan and avoiding high-calorie liquids like sugary beverages can significantly impact results.
Comparison with Other Diet Plans
Compared to traditional calorie-restricted diets, liquid diets often result in faster initial weight loss due to significant calorie reduction. For example, a study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that liquid diets led to more rapid weight loss in the first month compared to solid food diets. However, liquid diets may not be as sustainable in the long term and can lead to weight regain once regular eating patterns are resumed. Traditional diets that incorporate whole foods and gradual calorie reduction tend to support more sustainable weight loss and healthier eating habits.
The Science Behind Liquid Diet Weight Loss
Calorie Restriction and Metabolism
Liquid diets typically involve a substantial calorie deficit, prompting the body to use stored fat for energy. This leads to rapid weight loss; however, prolonged calorie restriction can slow down metabolism, making it harder to maintain weight loss. According to the New England Journal of Medicine, severe calorie restriction can reduce the basal metabolic rate by up to 20%, meaning the body burns fewer calories at rest.
Impact on Body Composition
While liquid diets can effectively reduce body fat, there is also a risk of losing muscle mass. Ensuring adequate protein intake is essential to preserve lean muscle tissue during the diet. A study published in The Journal of Nutrition highlighted that participants on a high-protein liquid diet maintained more muscle mass compared to those on a low-protein diet. Incorporating resistance training exercises can further help in preserving muscle mass during weight loss.
Hormonal Changes During Liquid Diets
Calorie restriction can influence hormone levels, including a decrease in leptin (which regulates hunger) and an increase in ghrelin (which stimulates appetite). These hormonal changes can make it challenging to adhere to the diet and maintain weight loss. Research in the International Journal of Obesity shows that hormonal shifts can increase hunger and reduce feelings of fullness, potentially leading to overeating once the diet is concluded.
Potential Benefits Beyond Weight Loss
Detoxification Claims (and Scientific Perspective)
Many proponents claim that liquid diets help detoxify the body by eliminating toxins. However, scientific evidence supporting detoxification benefits is limited, as the liver and kidneys naturally perform these functions efficiently. According to a review in Clinical Nutrition, there is no substantial evidence that liquid diets enhance the body’s detoxification processes beyond normal physiological functions.
Digestive System Rest
A liquid diet can give the digestive system a break from processing solid foods, potentially reducing inflammation and improving digestive health temporarily. This can be beneficial for individuals with digestive issues such as gastritis or diverticulitis. However, it’s important to reintroduce solid foods gradually to maintain digestive health in the long term.
Potential Improvements in Certain Health Markers
Some studies suggest that liquid diets may lead to improvements in:
- Blood Pressure: Reduction in body weight can lead to lower blood pressure levels, reducing the risk of hypertension.
- Cholesterol Levels: Weight loss can improve lipid profiles by lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol.
- Blood Sugar Control: Liquid diets may help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels, beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
A study published in Diabetes Care found that participants on a liquid diet experienced significant improvements in blood glucose levels and insulin sensitivity after 30 days.
Risks and Side Effects
Nutritional Deficiencies
Prolonged liquid diets may result in deficiencies in essential nutrients like iron, calcium, and vitamins B12 and D, impacting overall health and well-being. According to the Harvard School of Public Health, nutrient deficiencies can lead to anemia, weakened bones, and impaired immune function. It’s crucial to monitor nutrient intake and consider supplementation to prevent these deficiencies.
Muscle Loss Concerns
Without adequate protein intake, the body may break down muscle tissue for energy, leading to decreased muscle mass and strength. This not only affects physical appearance but also reduces metabolic rate, making weight maintenance more difficult. Ensuring sufficient protein in liquid meals and incorporating resistance training can help mitigate muscle loss.
Metabolic Slowdown
Extended calorie restriction can cause the metabolism to slow down, making it harder to maintain weight loss and potentially leading to weight regain. A study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that individuals on long-term calorie-restricted diets experienced a significant decrease in metabolic rate, which persisted even after weight loss was achieved.
Psychological Impacts
Strict liquid diets can be mentally challenging, leading to feelings of deprivation, irritability, and an unhealthy relationship with food. According to research published in Appetite, individuals on restrictive diets are more likely to experience mood swings and increased stress levels, which can impact overall quality of life and adherence to the diet.
Real-Life Experiences
Case Studies of 30-Day Liquid Diet Participants
Numerous individuals report significant weight loss within the first month of a liquid diet, often motivated by personal health goals or medical reasons. For example, Jane, a 35-year-old participant, lost 10 pounds in 30 days by following a meal replacement liquid diet, citing increased energy levels and improved digestion as additional benefits.
Before and After Comparisons
Before-and-after stories often showcase dramatic weight loss results, but it’s important to consider the long-term sustainability and overall health impacts beyond initial weight loss. Photos may show a significant reduction in weight, but without lifestyle changes, maintaining those results can be challenging.
Long-Term Follow-Ups (6 Months to 1 Year Later)
Long-term follow-ups reveal that many individuals struggle to maintain weight loss, emphasizing the need for sustainable lifestyle changes rather than short-term diet fixes. A follow-up study in The Lancet found that only 20% of participants maintained their weight loss one year after completing a liquid diet, highlighting the importance of ongoing support and healthy habits.
Conclusion
The 30-day liquid diet can offer quick weight loss results, making it an appealing option for those seeking rapid changes. On average, individuals can expect to lose between 8 to 12 pounds, with some experiencing more significant weight loss. However, the potential risks, including nutritional deficiencies, muscle loss, and metabolic slowdown, highlight the importance of approaching this diet with caution. While some may experience significant short-term benefits, long-term sustainability remains a challenge, with many individuals regaining weight post-diet.
FAQs
How much weight can I realistically lose on a 30-day liquid diet?
Weight loss results vary, but many people report losing 10-20 pounds during a 30-day liquid diet. However, a significant portion of this may be water weight and muscle mass, not just fat.
Is a 30-day liquid diet safe for everyone?
No, a 30-day liquid diet is not safe for everyone. It can be particularly risky for pregnant women, people with certain medical conditions, and those with a history of eating disorders. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any extreme diet.
How do I prevent nutrient deficiencies during a liquid diet?
Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, and protein sources in your liquid meals. Consider adding a multivitamin supplement, but consult with a healthcare provider first.
Are there any long-term health effects of a 30-day liquid diet?
Potential long-term effects can include nutrient deficiencies, muscle loss, and metabolic slowdown. Some people may also develop an unhealthy relationship with food.
Can I drink coffee or tea during a liquid diet?
Most liquid diets allow black coffee and unsweetened tea. However, avoid adding cream, sugar, or other caloric additives.