10 Key Signs of High Testosterone in a Man
Testosterone is often hailed as the driving force behind male vitality. It’s responsible for muscle mass, energy levels, and even mood regulation. But what happens when testosterone levels soar too high? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the signs of high testosterone in men, how it differs from low testosterone symptoms, and what you can do to maintain hormonal balance.

Understanding Testosterone Levels
Testosterone is a steroid hormone primarily produced in the testicles of men and, to a lesser extent, in the ovaries of women. It’s crucial for:
- Development of male reproductive tissues like the testes and prostate.
- Secondary sexual characteristics include increased muscle and bone mass and the growth of body hair.
- We are maintaining bone density, muscle strength, and mass.
- Sexual function and libido.
Normal Testosterone Levels
For adult men, normal testosterone levels typically range from 300 to 1,000 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). These levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day, peaking in the morning and declining in the evening. Factors influencing testosterone levels include:
- Age: Levels generally decrease with age.
- Lifestyle: Diet, exercise, and sleep patterns can impact production.
- Health Conditions: Obesity, diabetes, and hormonal disorders may affect levels.
Causes of High Testosterone
Elevated testosterone levels can result from various factors:
- Anabolic Steroid Use: Illicit use of anabolic steroids to enhance athletic performance or muscle growth can significantly increase testosterone levels.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): Overuse or misuse in treating low testosterone symptoms can lead to excessively high levels.
- Medical Conditions: Disorders such as adrenal tumors or testicular tumors can produce excess testosterone.
- Genetic Factors: Conditions like congenital adrenal hyperplasia affect hormone production.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): In women, PCOS can cause high testosterone levels, leading to symptoms like hirsutism and acne.
Understanding these causes is essential for effective management and treatment.
10 Key Signs of High Testosterone in a Man

Recognizing the signs of high testosterone can help you seek appropriate medical advice and maintain hormonal balance.
1. Increased Muscle Mass and Strength
One of the most noticeable signs is a rapid increase in muscle mass and strength. High testosterone levels enhance protein synthesis in muscle cells, leading to:
- Accelerated Muscle Growth: Gaining muscle mass more quickly than usual, even without significant changes in workout routines.
- Improved Strength: Lifting heavier weights or performing more repetitions with ease.
- Enhanced Physical Performance: Better endurance and reduced fatigue during physical activities.
Example: If you find yourself adding more weight to your lifts every week without plateauing, high testosterone might be a contributing factor.
Note: While increased muscle mass can be positive, sudden changes without proportional training may indicate hormonal imbalances.
2. Enhanced Sex Drive and Performance
Testosterone plays a key role in sexual function. Elevated levels can lead to:
- Increased Libido: A heightened interest in sexual activity and thoughts.
- Improved Erectile Function: Stronger and longer-lasting erections.
- Frequent Sexual Activity: Engaging in sexual activities more often.
Potential Issues:
- Hypersexuality: Compulsive sexual behavior that may interfere with daily life and relationships.
- Emotional Impact: Frustration or anxiety if desires are not met.
Advice: Open communication with your partner and seeking professional guidance can help manage these changes.
3. Aggressive Behavior and Mood Swings
Testosterone influences neurotransmitters that regulate mood. High levels may cause:
- Increased Irritability: Getting easily annoyed or angered by minor issues.
- Aggressive Tendencies: Exhibiting confrontational or hostile behavior.
- Mood Swings: Rapid fluctuations between emotional states, such as happiness, anger, and sadness.
Impact on Life:
- Strained Relationships: Conflicts with family, friends, or coworkers.
- Workplace Challenges: Difficulty collaborating or accepting feedback.
- Mental Health: Increased risk of anxiety or depression.
Action Steps:
- Stress Management: Incorporate relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
- Professional Support: Consider counseling or therapy to address emotional regulation.
4. Excessive Body and Facial Hair Growth
Testosterone stimulates hair follicles, leading to:
- Hirsutism: Unusually excessive hair growth on the face and body.
- Rapid Hair Growth: Needing to shave more frequently due to faster beard growth.
- New Hair Growth: Hair appearing in areas that were previously less hairy.
Considerations:
- Genetics: Family history plays a role in hair growth patterns.
- Cultural Factors: Societal perceptions of body hair vary.
Management:
- Grooming Practices: Regular shaving, waxing, or laser hair removal.
- Medical Evaluation: If hair growth is sudden or excessive, consult a healthcare provider.
5. Acne and Oily Skin
Elevated testosterone increases sebum production, which can clog pores:
- Persistent Acne: Breakouts on the face, back, and chest.
- Oily Skin: A shiny appearance, particularly in the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin).
- Skin Inflammation: Redness and tenderness due to acne.
Management Tips:
- Skincare Routine: Use non-comedogenic products, cleanse twice daily, and exfoliate regularly.
- Professional Help: Dermatologists can offer treatments like topical retinoids or oral medications.
Note: Acne can affect self-esteem, so addressing it promptly is important.
6. Deep Voice and Prominent Adam’s Apple
Testosterone affects the vocal cords and larynx:
- Deeper Voice: A noticeable drop in pitch and tone.
- Prominent Adam’s Apple: Enlargement of the larynx makes Adam’s apple more visible.
- Voice Changes: Hoarseness or instability in vocal quality.
Observation:
- Puberty vs. Adulthood: Voice deepening is normal during puberty, but significant changes in adulthood may signal hormonal fluctuations.
Recommendation: Seek medical advice if you experience unexpected voice changes.
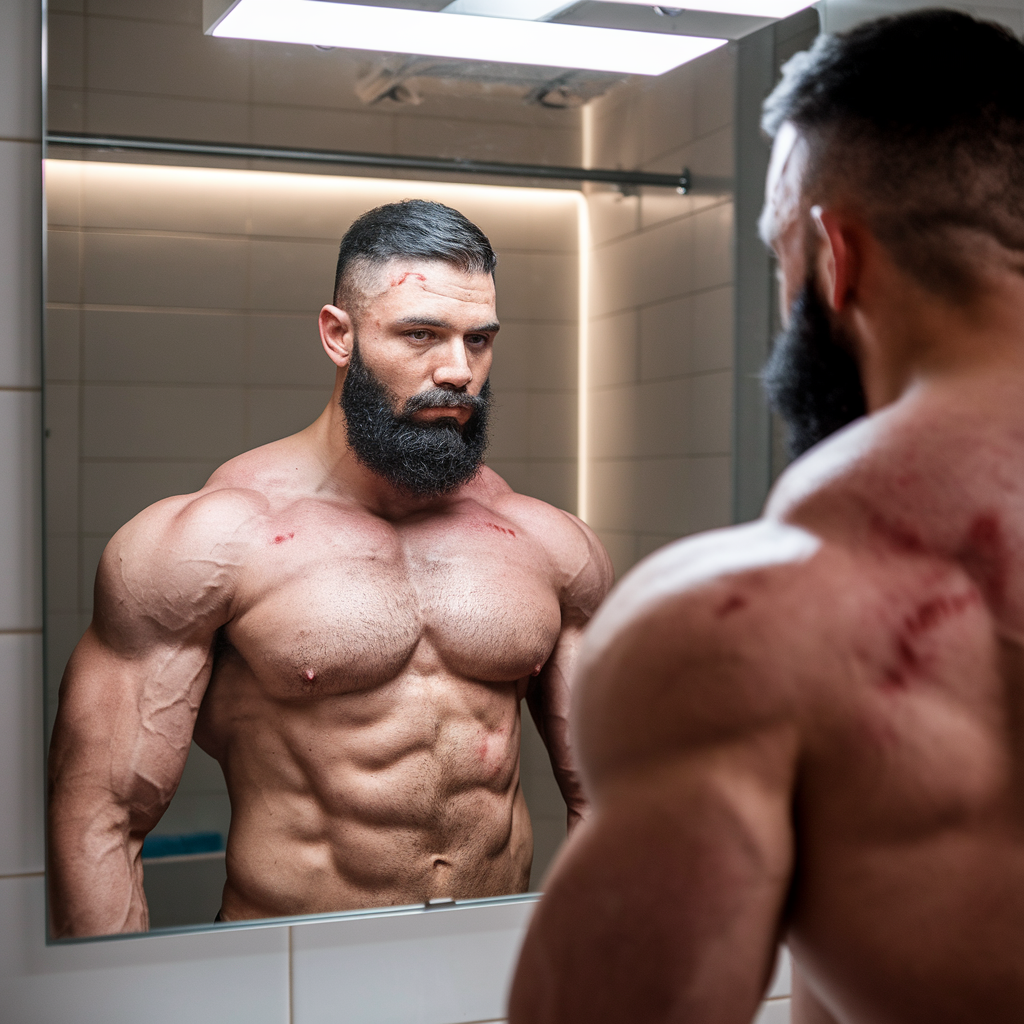
7. Male Pattern Baldness
High levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone, can lead to hair loss:
- Receding Hairline: Hair loss at the temples forming an “M” shape.
- Thinning Crown: Bald spots on the top of the head.
- Overall Thinning: Hair becomes finer and less dense across the scalp.
Treatment Options:
- Medications: Minoxidil (Rogaine) or finasteride (Propecia) may slow hair loss.
- Hair Transplants: Surgical option for restoring hair.
- Lifestyle Changes: Diet and stress reduction can support hair health.
Advice: Early intervention can improve treatment effectiveness.
8. Increased Confidence and Risk-Taking Behavior
Testosterone influences the brain’s reward pathways:
- Boosted Confidence: Feeling more self-assured and assertive.
- Risk-Taking: Engaging in adventurous or potentially dangerous activities.
- Competitive Nature: Strong desire to win or outperform others.
Positive Aspects:
- Leadership Qualities: Confidence can inspire and motivate others.
- Innovation: Willingness to take calculated risks may lead to success.
Negative Aspects:
- Impulsivity: Making hasty decisions without considering consequences.
- Legal and Financial Risks: Involvement in reckless behaviors like gambling or unsafe driving.
Suggestion: Balance confidence with caution by evaluating risks and seeking advice when necessary.
9. Improved Cognitive Abilities
Some research suggests a link between testosterone and cognitive function:
- Enhanced Spatial Skills: Better at visualizing and manipulating objects in space.
- Quick Problem-Solving: Faster at analyzing situations and finding solutions.
- Sharp Memory: Improved recall of information and experiences.
Applications:
- Professional Advantages: Fields like engineering, architecture, or strategy-based roles.
- Everyday Benefits: Easier navigation, assembling objects, or understanding complex diagrams.
Caution: Cognitive improvements should be balanced with thoroughness to avoid overlooking details.
10. Higher Red Blood Cell Count
Testosterone stimulates erythropoietin production, increasing red blood cells:
- Enhanced Endurance: Better oxygen delivery enhances physical performance.
- Polycythemia Risk: Excessive red blood cells can thicken the blood.
- Health Concerns: Increased risk of blood clots, stroke, or heart attack.
Monitoring:
- Regular Blood Tests: Check hematocrit and hemoglobin levels.
- Medical Intervention: Treatments like therapeutic phlebotomy may be necessary.
Warning: Symptoms like headaches, dizziness, or blurred vision require immediate medical attention.
Distinguishing High Testosterone from Low Testosterone Symptoms
Understanding the difference between high and low testosterone symptoms is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Low Testosterone Symptoms
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness despite adequate rest.
- Decreased Libido: Reduced interest in sexual activity.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty achieving or maintaining erections.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or lack of motivation.
- Loss of Muscle Mass: Decreased strength and muscle tone.
- Increased Body Fat, Especially around the abdomen.
- Reduced Bone Density: Higher risk of fractures.
High Testosterone Signs
- Aggressiveness: Increased irritability and aggressive behavior.
- Excessive Hair Growth: Unusual patterns or rapid growth on the body and face.
- Acne and Oily Skin: Persistent skin issues.
- Enhanced Libido: Overactive sexual desire.
- Risk-Taking Behavior: Engaging in potentially harmful activities.
Recommendation: If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for hormone testing and personalized guidance.
RELATED: Signs of Gaining Muscle and Losing Fat
Women with High Testosterone: A Brief Overview
While testosterone is primarily a male hormone, women produce it in smaller amounts. Women with high testosterone may experience:
- Hirsutism: Excessive facial and body hair.
- Acne: Particularly along the jawline and chin.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Infrequent or absent periods.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A common endocrine disorder linked to high testosterone.
- Infertility: Difficulty conceiving due to hormonal imbalances.
- Weight Gain: Particularly around the abdomen.
Health Implications:
- Metabolic Issues: Increased risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Emotional Effects: Anxiety, depression, or mood swings.
Recommendation: Women experiencing these symptoms should seek medical evaluation for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if you notice:
- Persistent Symptoms: Any signs of hormonal imbalance that affect your quality of life.
- Sudden Changes: Rapid shifts in mood, appearance, or physical abilities.
- Health Concerns: Symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or severe headaches.
Potential Risks of Untreated High Testosterone
- Cardiovascular Problems: Elevated risk of heart disease and hypertension.
- Liver Damage: Particularly from anabolic steroid use.
- Sleep Apnea: Breathing interruptions during sleep.
- Psychological Effects: Increased risk of depression, anxiety, or aggressive behavior.
- Infertility: Hormonal imbalances can affect sperm production.
Medical Evaluation
- Hormone Testing: Blood tests to measure testosterone and other hormone levels.
- Physical Examination: Assessing symptoms and overall health.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasounds or MRIs if tumors are suspected.
Importance: Early detection and treatment can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Natural Ways to Balance Testosterone Levels
Maintaining hormonal balance involves holistic lifestyle choices.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate aerobic activities and strength training.
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours per night to support hormone regulation.
- Stress Reduction: Practice mindfulness, meditation, or yoga to lower cortisol levels.
- Avoid Substance Abuse: Limit alcohol consumption and avoid tobacco and illicit drugs.
Tip: Consistency is key; make gradual changes for sustainable results.
Dietary Considerations
- Balanced Nutrition: Emphasize whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Healthy Fats: Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids like salmon, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Limit Processed Foods: Reduce intake of sugars, refined carbs, and trans fats.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
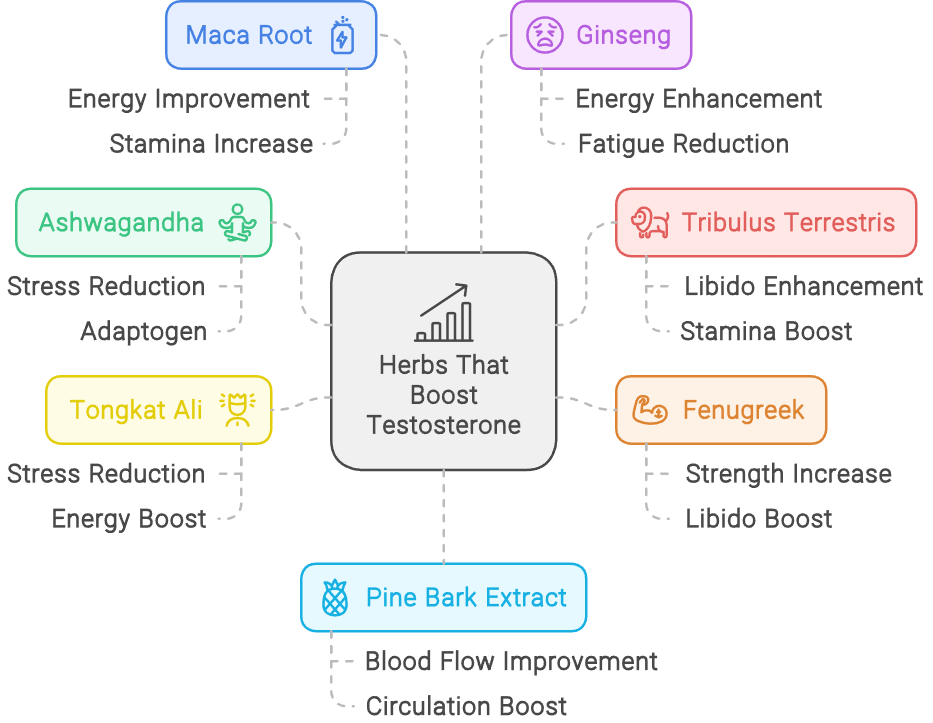
- Herbal Supplements: Some herbs like spearmint and licorice root may help lower testosterone levels.
Foods That May Influence Testosterone
- Lower Testosterone:
- Soy Products: Contain phytoestrogens that may reduce testosterone.
- Flaxseed: High in lignans, which can impact hormone metabolism.
- Green Tea: Contains antioxidants that may balance hormones.
- Increase Testosterone:
- Zinc-rich foods: Oysters, beef, and pumpkin seeds support testosterone production.
- Vitamin D Sources: Fatty fish and fortified foods help maintain levels.
Consultation: Always speak with a healthcare provider before starting new supplements or making significant dietary changes.
Maintaining hormonal balance is vital for overall health and well-being. Testosterone levels that are too high or too low can lead to significant physical and emotional symptoms.
FAQ
Can high testosterone levels be harmful?
Yes, excessively high testosterone can lead to health issues such as heart disease, liver damage, and increased risk of aggressive behavior. It’s important to manage hormone levels under medical supervision.
How is high testosterone diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examinations, assessment of symptoms, and blood tests measuring testosterone and other hormone levels.
Can women have high testosterone levels?
Yes, women can experience high testosterone, leading to symptoms like acne, hirsutism, menstrual irregularities, and PCOS.
Is it safe to use testosterone boosters?
Using testosterone boosters without medical supervision can be dangerous, leading to hormonal imbalances and associated health risks.
Can stress affect testosterone levels?
Yes, chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, which may negatively impact testosterone production.